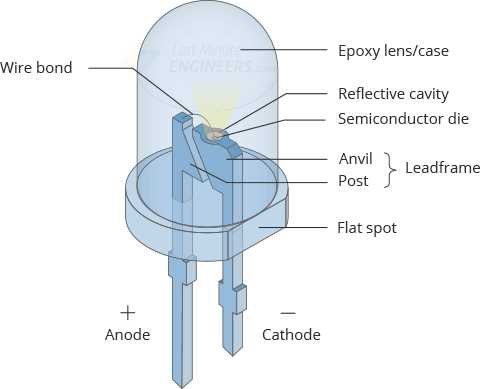
LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
• LED is specially prepared pn junction diode which operated in forward bias.
• Under forward bias conditions, it can emit radiation by electro luminescence in the UV,visible or infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum (beacause of recombination of electrons and holes)
• The quanta of light energy released is approximately proportional to the band gap of the semiconductor (energy gap > 1.8 eV.)
• The IV characteristics of an LED is dependent on the color that is chosen some of them are shown in the below table
|
Color |
Wavelength [nm] |
Voltage drop [ΔV] |
Semiconductor material |
|
|
λ > 760 |
ΔV < 1.63 |
Gallium
arsenide
(GaAs) |
||
|
610 < λ < 760 |
1.63 < ΔV < 2.03 |
Aluminium
gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) |
||
|
590 < λ < 610 |
2.03 < ΔV < 2.10 |
Gallium
arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) |
||
|
570 < λ < 590 |
2.10 < ΔV < 2.18 |
Gallium
arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) |
||
|
500 < λ < 570 |
1.9[70] < ΔV < 4.0 |
Traditional
green: |
||
|
450 < λ < 500 |
2.48 < ΔV < 3.7 |
Zinc
selenide
(ZnSe) |
||
|
400 < λ < 450 |
2.76 < ΔV < 4.0 |
Indium gallium nitride (InGaN) |
||
|
|
Multiple types |
2.48 < ΔV < 3.7 |
Dual
blue/red LEDs, |
|
|
|
λ < 400 |
3.1 < ΔV < 4.4 |
Diamond
(235 nm)[71] |
|
|
|
Multiple types |
ΔV ~ 3.3[76] |
Blue
with one or two phosphor layers: |
|
|
White |
Broad spectrum |
ΔV = 3.5 |
Blue/UV diode with yellow phosphor |
• LED Activation chart for different colours
|
|
Voltage |
Amperes |
|
Red |
1.882 |
0.0021 |
|
Green |
1.89 |
0.0021 |
|
Yellow |
1.819 |
0.0021 |
|
Blue |
2.64 |
0.0021 |
Applications of LED
1. LED used in burglar alarms.
2. Seven-segment display of LED used as an Indicator
3. LED used in ON-OFF switch.
Advantages of LED’s
1. Very low voltage and current are enough to drive the LED. (Voltage range- 1 to 2 volts.)
2. The response time is very less- only about 10 nanoseconds.
3. The device does not need any heating and warm up time.
4. Miniature in size and hence light weight.
5. An LED has a life span of more than 20 years.
Disadvantages of LED’s
1. A slight excess in voltage or current can damage the device.
2. The device is known to have a much wider bandwidth compared to the laser.