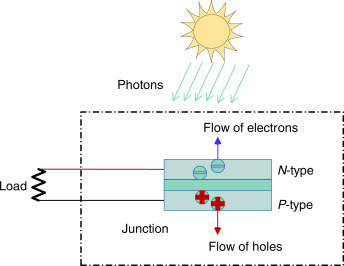
• Photovoltaic cells consist of two or more layers of semiconductors with one layer containing positive charge and the other negative charge lined adjacent to each other.
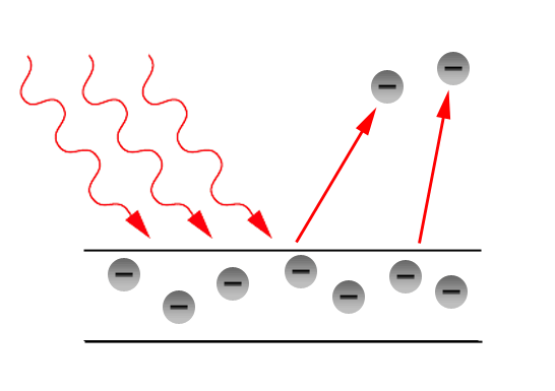
• Photons (sunlight particles), hits the cell and is either reflected, transmitted, or absorbed.
• When the photons are absorbed by the negative layer of the photovoltaic cell, the energy of the photon gets transferred to an electron in an atom of the cell.
• With the increase in energy, the electron escapes the outer shell of the atom. The freed electron naturally migrates to the positive layer creating a potential difference between the positive and the negative layer. When the two layers are connected to an external circuit, the electron flows through the circuit, creating a current.